Geomembrane Types Uses and Installation Guide

Many projects that need to hold water or chemicals rely on a plastic liner called a geomembrane. When the wrong liner is chosen or it is fitted poorly, leaks can happen, water is lost, and the soil or water nearby can become polluted.
This short guide shows the main geomembrane types, common uses, and the basic steps for proper installation and testing. Read on to get clear, simple advice that helps you pick the right liner and avoid common problems.
What Is a Geomembrane?
When people build landfills, ponds, or chemical storage areas, they need a way to stop liquids from leaking into the soil. If leaks happen, groundwater gets dirty, animals suffer, and fixing the mess costs a lot. This is where a geomembrane steps in. Think of it as a giant plastic sheet that acts like a waterproof shield for the ground.
A geomembrane is usually made from synthetic plastic materials. It comes in rolls, is spread out over large areas, and then joined together to form one big liner. The thickness often ranges between 0.5 mm and 3.0 mm. Thicker sheets are stronger and last longer, while thinner ones are easier to handle.
The main job of this liner is simple: keep liquids in their place. Whether it is dirty water from a landfill, salty water in a fish pond, or chemicals from a mining site, the sheet creates a barrier. This helps protect soil, rivers, and underground water. In many countries, using geomembranes is not just smart but also required by law to keep the environment safe.
Because the uses are wide, there are different materials available, each with its own strengths. Some are stiff and tough, while others are softer and bend easily. Picking the right type is important because using the wrong one can lead to early damage or leaks. And no one wants to see fish swimming where garbage is buried.
Types of Geomembrane Materials
Now that we know what a geomembrane is, the next question is: what types are out there? Not all liners are the same. Each material works best in certain conditions, and choosing the right one can save both money and headaches. Let’s look at the most common types one by one.
HDPE Geomembrane
High-density polyethylene, or HDPE, is the most popular choice. It is strong, resists chemicals, and lasts a long time. This makes it perfect for landfills, wastewater plants, and mining areas. However, it is less flexible, so handling and fitting it on uneven ground can be a little harder.
Clients who need reliable strength often choose NovaSeal® HDPE from Novageo Asia. It meets international standards like GRI-GM13 and is trusted for tough jobs. In simple terms, if you need a heavy-duty shield, this is the go-to option.
LLDPE Geomembrane
Linear low-density polyethylene, or LLDPE, is more flexible than HDPE. It can adjust better to curves, bends, and uneven soil. This makes it a good choice for ponds, canals, or floating covers. While it is not as stiff as HDPE, its ability to bend without breaking is a big advantage during installation.
Think of it like comparing a thick cardboard to a bendy sheet of rubber. Both block water, but one is easier to fold around corners.
PVC Geomembrane
Polyvinyl chloride, or PVC, is lightweight and easy to handle. It is also simple to repair if damage occurs. Many people use it for tunnels, covers, or temporary liners. On the downside, it may not last as long as HDPE in harsh chemical settings.
PVC works well when projects need a quick, easy, and budget-friendly solution. For farmers or small pond owners, it can be the practical choice.
Other Options: PP and EPDM
Some special projects use polypropylene (PP) or ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM). These are less common but useful in certain cases. PP offers good resistance to heat, while EPDM is very flexible and often used in roofing or decorative ponds.
These types are not needed in every job, but when conditions demand something special, they can be the right fit.
Common Uses of Geomembranes
Geomembranes are used anywhere liquid needs to stay in or stay out. Here are some of the most common applications:
- Landfills – prevent toxic leachate from leaking into the ground.
- Mining – line tailing ponds and heap leach pads to stop chemical spills.
- Water reservoirs – store drinking water or irrigation water without seepage.
- Ponds and aquaculture – fish farms and decorative ponds stay clean and safe.
- Wastewater treatment – line tanks and lagoons to avoid contamination.
- Canals – reduce water loss through seepage in irrigation canals.
Each of these uses depends on picking the right material, thickness, and installation method. For example, landfills usually need strong HDPE liners, while ponds may use flexible LLDPE.
Advantages of Using Geomembranes
So, why do so many industries rely on geomembranes? Here are the key benefits:
- Leak prevention – acts as a barrier that keeps liquids where they belong.
- Environmental protection – stops harmful chemicals from polluting soil and groundwater.
- Cost-effective – reduces repair, water loss, and long-term maintenance costs.
- Durability – materials like HDPE last decades under harsh conditions.
- Flexibility in use – different types suit different industries and projects.
In short, geomembranes provide peace of mind. They protect the environment, save money, and make projects safer and more reliable.
Different Types of Geomembranes
Not all geomembranes are the same. Each type serves a different purpose depending on strength, flexibility, and resistance. The most common types include:
- HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) – strong, durable, and resistant to chemicals. Best for landfills and mining.
- LLDPE (Linear Low-Density Polyethylene) – more flexible than HDPE, useful for ponds and reservoirs.
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) – easy to install, commonly used in smaller water projects.
- EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) – very flexible, often used for decorative ponds and irrigation canals.
Choosing the right geomembrane depends on the project. For large-scale industrial needs, HDPE is often the top choice. For smaller, flexible uses, LLDPE or PVC may be more practical.
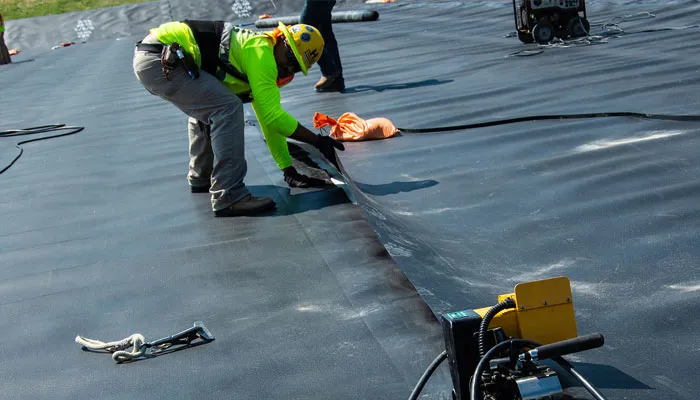
How Geomembranes Are Installed
Installing geomembranes requires skill because even small errors can cause leaks. The general steps include:
- Surface preparation – clear the ground of rocks and debris.
- Unrolling the liner – geomembranes are spread across the prepared surface.
- Seaming – panels are joined using heat welding or adhesives to prevent leaks.
- Inspection – seams and surfaces are checked for any damage.
- Covering (if needed) – in some cases, soil or protective layers are added on top.
Professional installation is always recommended. Companies like Novageo Asia provide high-quality materials and trained teams to ensure the geomembrane performs reliably for years.
Maintenance and Care of Geomembranes
Even though geomembranes are built to last, regular care helps them stay effective for longer. Some key practices include:
- Frequent checks – look for holes, tears, or areas where the liner may have shifted.
- Cleaning – remove sharp objects, debris, or buildup that may weaken the surface.
- Quick repairs – fix small damages right away before they spread.
- Protective layers – in high-traffic areas, adding soil or mats above the liner helps reduce wear.
Simple maintenance steps save money in the long run by avoiding major replacements.
Choosing the Right Supplier
The quality of a geomembrane depends heavily on where it comes from. A trusted supplier provides not just the liner but also guidance on the right type for each project.
When selecting a supplier, look for:
- Proven experience in geomembrane projects
- Range of products like HDPE, LLDPE, and PVC liners
- Technical support and installation services
- Strong customer reviews and project history
Novageo Asia offers both quality geomembrane products and expert support, making it a reliable choice for projects across different industries.
Benefits of Using Geomembranes
Geomembranes solve common leakage and containment problems in many industries. Some clear benefits include:
- Leak prevention – acts as a strong barrier against water, waste, and chemicals.
- Cost savings – reduces water loss and protects soil, avoiding expensive fixes later.
- Flexibility – available in different thicknesses and materials for small ponds to large landfills.
- Durability – resistant to weather, UV rays, and many chemicals.
| Benefit | Why It Matters |
| Leak Prevention | Keeps liquids safely contained |
| Cost Savings | Avoids expensive repairs or losses |
| Flexibility | Fits many project types and scales |
| Durability | Long life even in harsh conditions |
Conclusion
Geomembranes are a simple but effective solution for projects that need reliable liquid control. Picking the right type, installing it properly, and working with a trusted supplier like Novageo Asia ensures long-lasting results.
Q1: How long do geomembranes last?
Most high-quality geomembranes last 20–30 years with proper care.
Q2: Can geomembranes be repaired if damaged?
Yes, small tears or holes can be fixed using patches or welding.
Q3: Where are geomembranes most commonly used?
They are used in landfills, mining, ponds, reservoirs, and construction sites.
Q4: What thickness is best for a pond liner?
Usually 1.0–1.5 mm thick geomembranes work well for ponds.